What are the differences between var, let and const in Javascript?
There are three ways to declare variables in Javascript, but what are the real differences ?
Article publié le 08/02/2021, dernière mise à jour le 22/09/2023
Javascript has been originally created with only one keyword to declare a variable, this reserved word is: var.
But since the 6th version (ECMAScript 2015) of the language specification, two new keywords appeared: let and const.
If I had to summarize the definition of these two new ways for declaring variables, I could say that:
- let is to declare a local variable
- const is to declare a constant variable
Be careful, a constant reference doesn't mean that the value behind the reference is immutable, only that the reference can't be changed.
But let's discover how these variables work differently in practice:
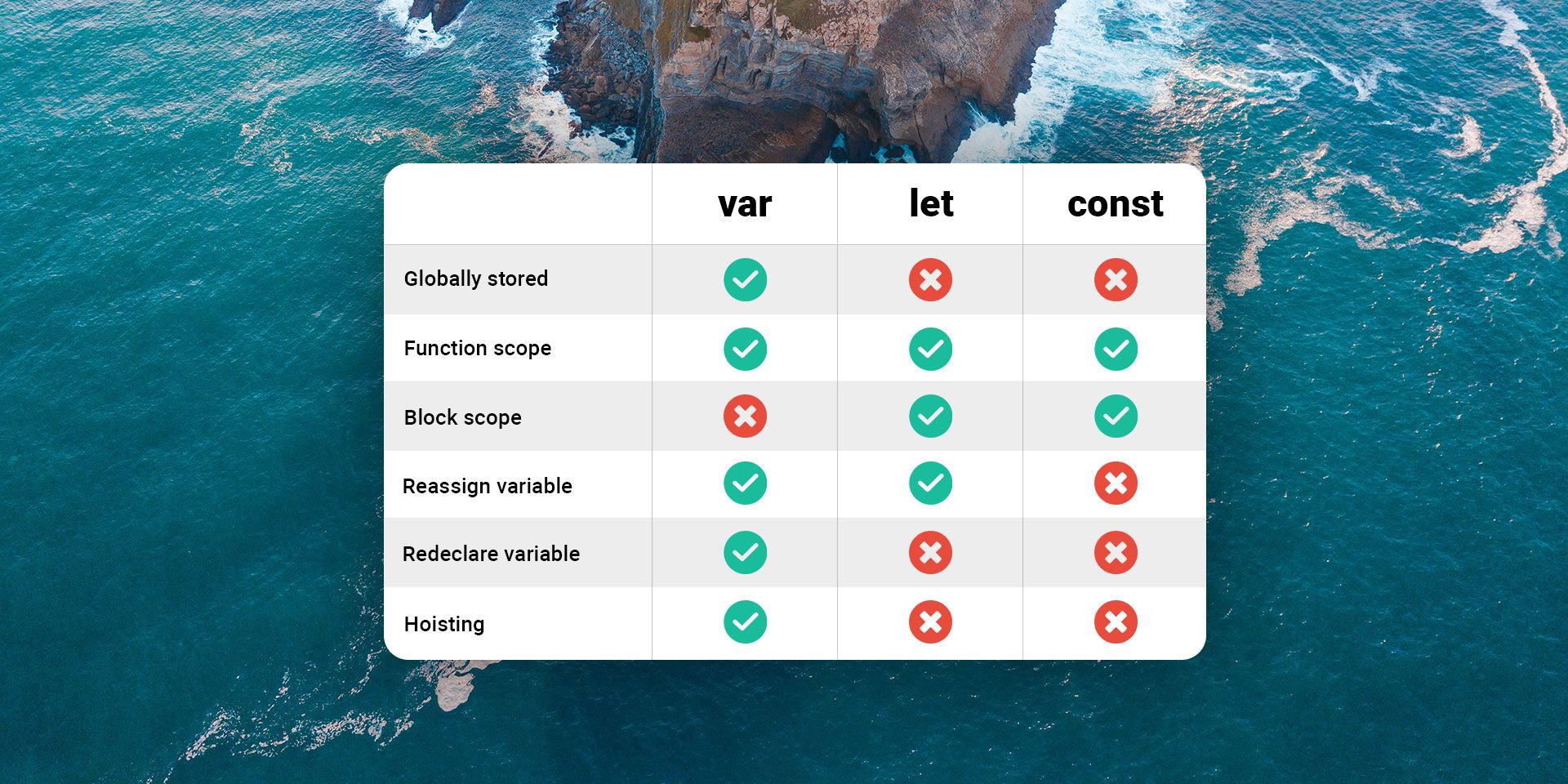
Store globally?
- var : yes✔️
- let : no ❌
- const : no ❌
When var is used to delcare a variable outside of a function, then this variable will be referenced in the global object of the script.
In the browser, this variable is called "window" and in a NodeJS environment it's called "global".
Limited to function scope?
- var : yes ✔️
- let : yes ✔️
- const : yes ✔️
The scope of a function is the only one to put all the variables on an equal footing and declaring one inside of a function won't have any effect on the outside variables.
Limited to block function?
- var : no ❌
- let : yes ✔️
- const : yes ✔️
To those who wonder what a block is, it simply is a group of instructions written between a pair of curly brackets "{...}" except when they delimiting a function body or a JSON object.
A set of instruction is ofter found after an if, else, for, while, etc. Remember that a variable declared using "var" inside a for will automatically be considered as global.
Excepted if the for is inside a function, obviously.
Can be reassigned?
- var : yes ✔️
- let : yes ✔️
- const : no ❌
Reassigning means either changing the value of the variable when we're using primitive types, or modifying the variable reference when using a complex type.
Do note that if const is used to reference an object, the content of this object can still be modified.
Can be redeclared?
- var : yes ✔️
- let : no ❌
- const : no ❌
Redeclaring a variable is impossible excepted if using var, but it's definitely not a good practice and I advise you not to do it.
Hoisting?
- var : yes ✔️
- let : no ❌
- const : no ❌
Hoisting is a more complex mechanism which happens during JS code interpretation, and if you're not familiar with this concept, I recommand you to read my dedicated blog post about it (french) !
Aucun commentaire pour l'instant